ElectroMechanical Transduction
The concurrence of electrical and mechanical signals to orchestrate a cascade of physiological events including nerve signaling and sensory organ function in order to modulate pain, accelerate tissue healing, resolve inflammation, alter arthrogenic muscle inhibition and improve muscle function.

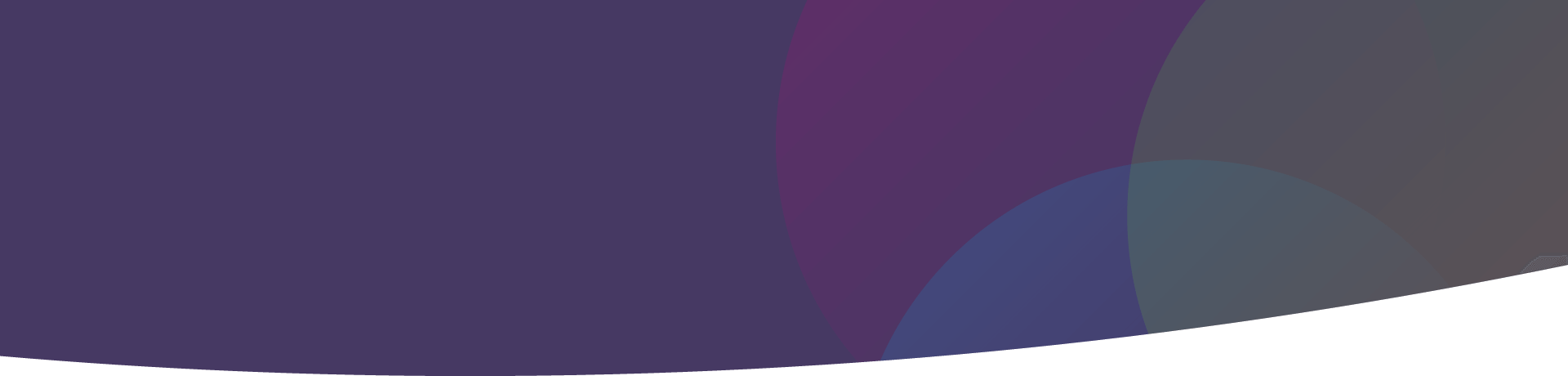
Nerve Desensitization with Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Current
Employed to effectively halt the transmission of pain signals and induce sedation in sensory nerves. This innovative approach grants durable alleviation from incapacitating pain prevalent in conditions like trigeminal neuralgia, enhancing the quality of life for individuals afflicted by such ailments.
Learn More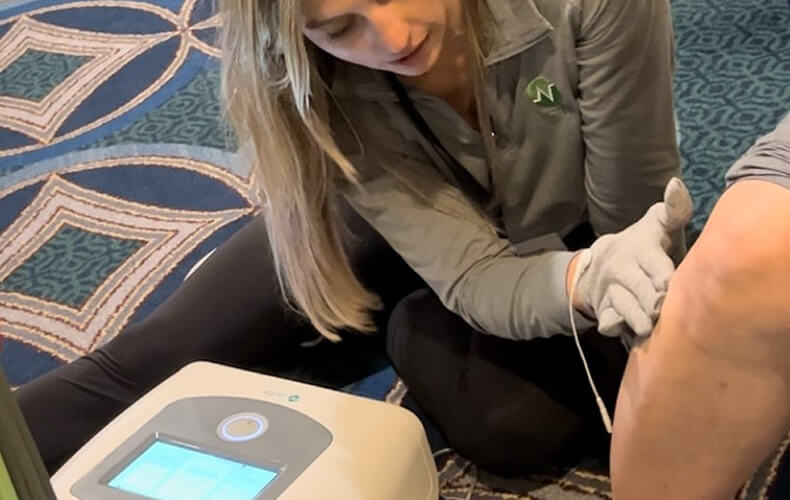
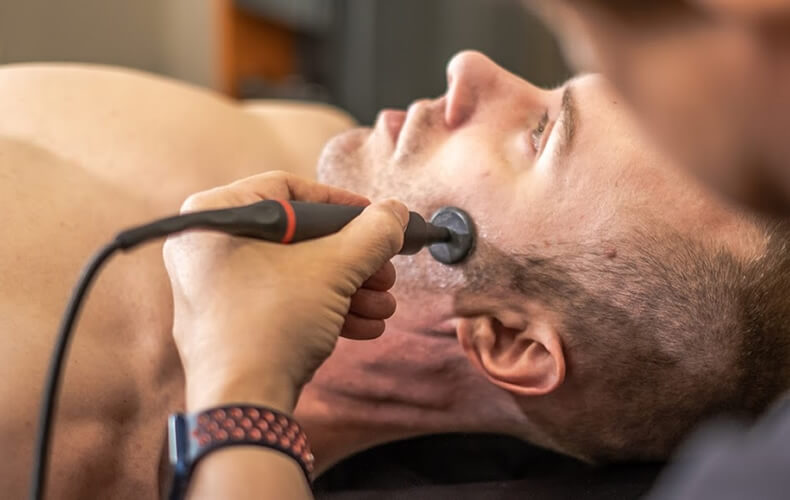
Motor Point Mapping with Conductive Glove and Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
The strategic identification of Motor Points prior to employing neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) offers potential for diminishing current levels needed for muscle activation, thus reducing discomfort while optimizing muscle fiber recruitment and tension generation. Recent findings suggest that a personalized approach for patients could elevate clinical protocols and refine NMES implementation. Consequently, integrating the methodical Motor Point mapping process into NMES clinical utilization is advised for achieving enhanced and favorable therapeutic results.
Learn More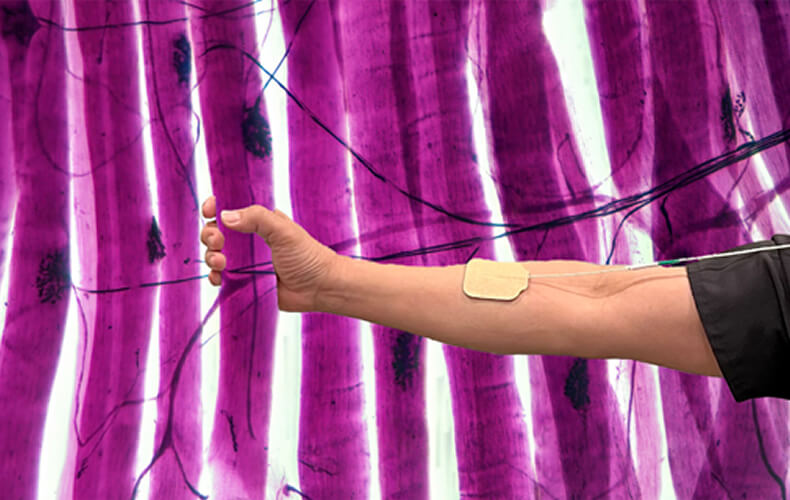
Management of Arthrogenic Muscle Response with Electrotherapy
Arthogenic Muscle Inhibition (AMI), an ongoing reflex inhibition, safeguards joints after injury by limiting muscle activity via inhibitory interneurons. While pain and disuse contribute to muscle atrophy, mechanoreceptor activity primarily drives AMI. This mechanism impedes joint rehab, causing reduced range of motion, muscle wasting, and weakness. Athletes' return to competition with functional deficits and injury susceptibility is due to AMI's role. Blocking AMI could optimize athlete return post-injury. Academic literature suggest that electrophysical agents (EPAs) are effective in altering arthrogenic muscle inhibition (AMI) due to its therapeutic effect of mitigating inflammation, modulating pain and decreasing joint tightness which leads to accelerated healing and improvement in functional mobility.
Learn More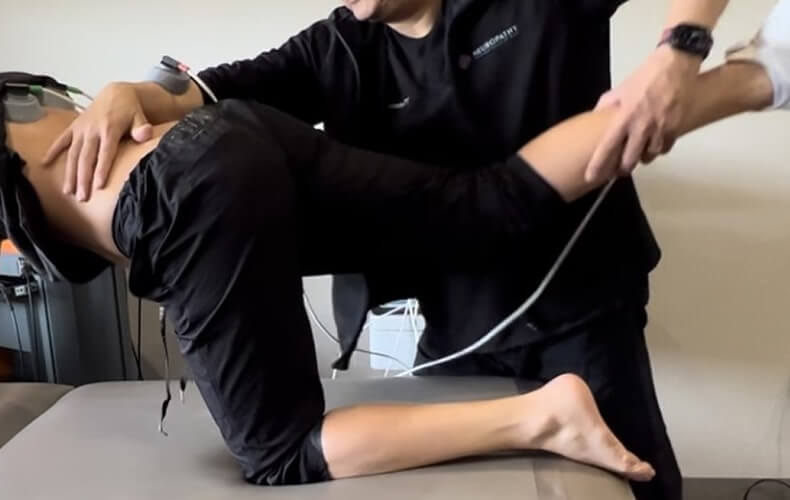
Electric Cell Signaling (EcST)
A modern advancement in electrotherapy that utilizes non-invasive electrical stimulation to facilitate cellular communication and promote healing. By delivering targeted electric pulses to cells and tissues, Electric Cell Signaling Treatment aims to restore proper signaling pathways, aiding in pain management and enhancing overall well-being. This innovative approach harnesses the body's innate ability to transmit electrical signals, offering a potential solution for various conditions by optimizing cell function and signaling processes, leading to improved health outcomes.
Learn More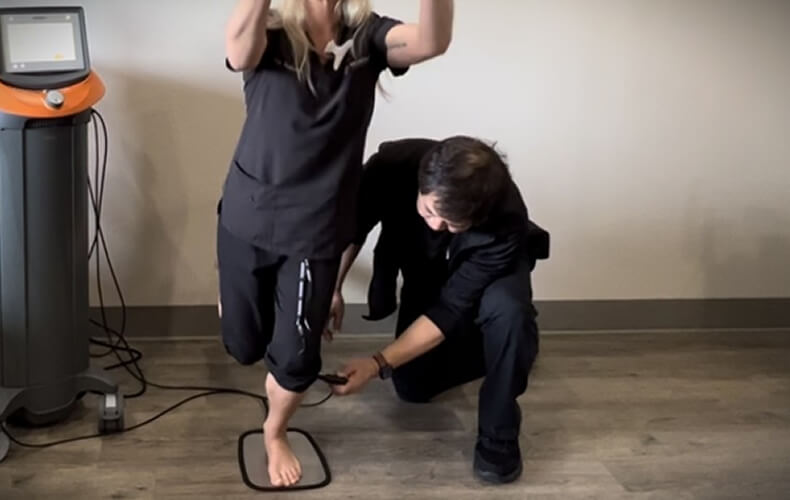
Neuromuscular Reeducation concurrent with pain modulation with TECAR Therapy
High-frequency electromagnetic fields with capacitive and resistive electrodes in therapy has been confirmed to significantly elevate treatment region temperature effectively sedating sensory nerves. This allows pain free joint movements necessary for anti-gravity loading during neuromuscular reeducation exercises. TECAR has practical implications for optimizing physiotherapy sessions. Studies recommend further inquiry, including clinical trials and assessing physiological responses like circulation and tissue temperature. Research deepens the understanding of high-frequency electromagnetic fields, electrode types, and thermal reactions, paving the way for improved therapeutic approaches.
Learn More
Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM)
IASTM involves using tools to eliminate scarring from injured soft tissues, promoting healing via new extracellular matrix proteins like collagen. It's increasingly used in sports rehab and athlete training. Studies indicate IASTM enhances soft tissue function, range of motion, and reduces pain post sports injuries. It's believed to hasten recovery and return to sports. Clinicians in our clinics are Graston Technique Specialists (GTS).
Learn More
Running Gait Analysis with 3D Helix System
Understanding the biomechanics of running unveils crucial insights into optimizing performance and minimizing injury risks. Gait and strength profoundly influence running risks, as poor mechanics strain joints and tissues. Efficient mechanics, conversely, enhance running economy, conserving energy. Vital to this is the role of footwear. Proper shoes provide support, alignment, and cushioning, aligning with individual mechanics. Embracing optimal mechanics, coupled with proper footwear, promotes a balanced, injury-resistant stride, elevating the joy and benefits of running.
Learn More
Heart Rate Variability Monitoring
HRV measures the time gaps between heartbeats, reflecting cardiovascular adaptability. It's controlled by the autonomic nervous system's sympathetic and parasympathetic balance. Physical therapists use vagus nerve stimulation to enhance parasympathetic activity and HRV. The vagus nerve manages bodily functions, including HRV, through sensory and motor fibers. Vagus nerve stimulation involves electrically stimulating specific nerve areas to modulate autonomic balance, improving HRV and overall function.
Learn More

